EPC Ratings

Are you buying, selling, or renting a property? If so, you’ll almost certainly come across something called an Energy Performance Certificate (EPC). In this guide, we’ll talk you through everything there is to know about it.
What is an Energy Performance Certificate?
An Energy Performance Certificate (EPCs) is an official document that displays the energy efficiency and environmental impact of a building, graded from A (very efficient) to G (inefficient). The certificate evaluates things like insulation, heating systems and lighting, giving homeowners and buyers an idea of how much energy a property uses and how much it might cost to run. In addition, EPCs also offer recommendations on how to make a home more energy-efficient, which can help to lower bills and reduce carbon emissions.
What information does an EPC show?
EPCs may vary in appearance depending on when and where they are issued, but they all contain the same information:
- Information about the property, including the address, type of property, total floor area, date of assessment and date of certificate.
- The estimated energy costs of the building for the next 3 years and the cost of potential savings.
- The energy efficiency rating of the building.
- A summary of the property’s energy performance features (walls, roof, lighting, windows, heating, etc.).
- Information about the government’s Green Deal scheme.
- A list of recommended measures you could undertake to improve the energy performance of your home, as well as the indicative cost, estimated savings per year and the EPC rating after carrying out the works.
- Details about the person who carried out the EPC assessment.
- Information about your home’s heat demand.
What are the EPC bandings?
Energy Performance Certificates rate a property’s energy efficiency on a scale from A to G, with A being the most efficient and G the least. Using the government's Standard Assessment Procedure (SAP), a property is given a score from 1 to 100, which corresponds to the following bands:
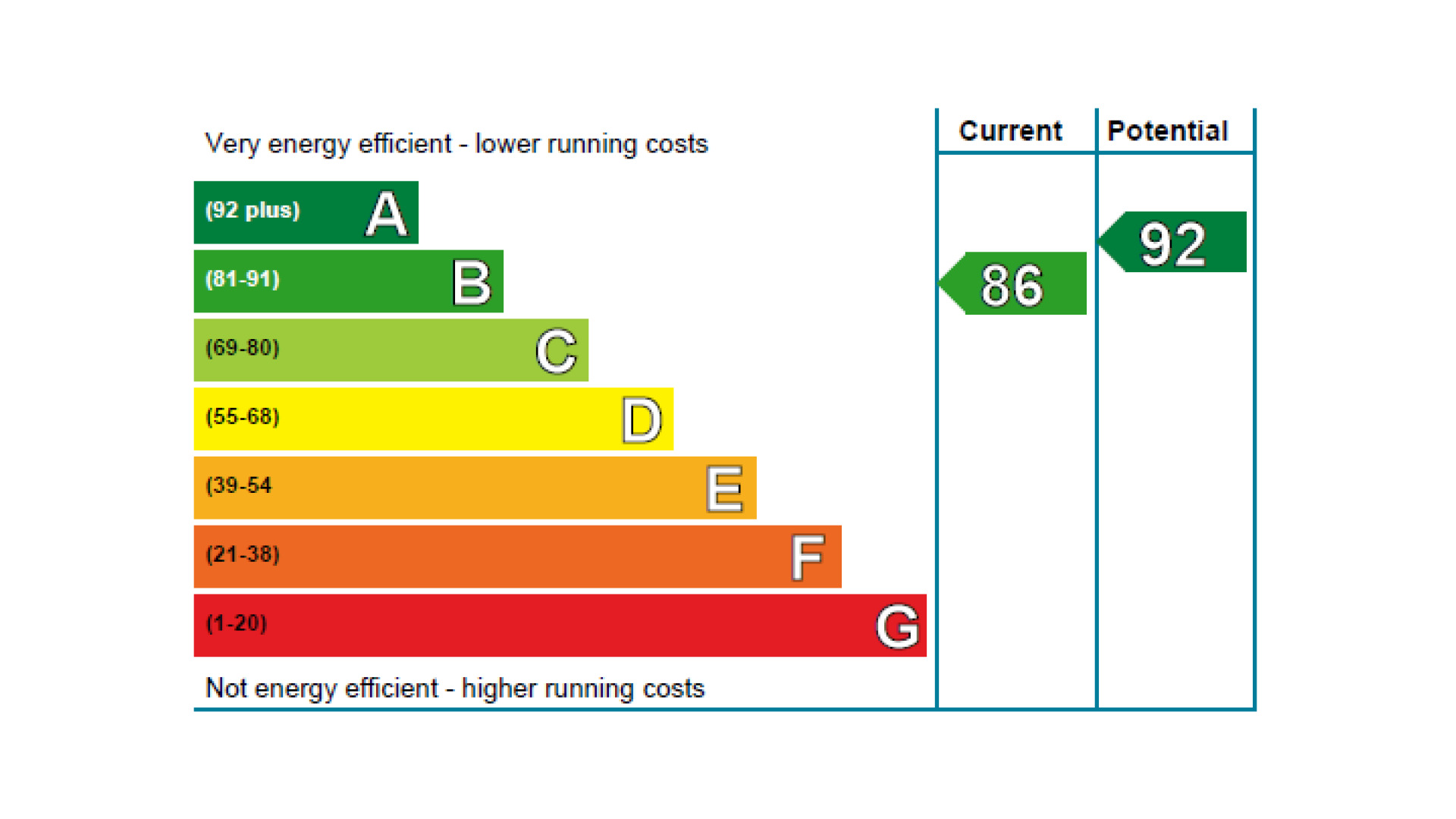
How is an Energy Performance Certificate rating calculated?
An EPC assessment involves a qualified energy assessor visiting your property, where they'll inspect aspects like the heating system, insulation and even the light bulbs you use. The assessor then calculates a score based on energy consumption, cost and environmental impact.
How long does an EPC assessment take?
An EPC assessment typically takes around 30-60 minutes, depending on the size of the property. The assessor will inspect different areas, take some measurements and complete the energy assessment before issuing your rating. It’s a quick process, and you’ll usually get your EPC report within a few days.
What does an EPC cost?
EPC costs can vary depending on the type of property, size and location, but you can expect to pay between £60 and £120. The good news? Once it’s done, you won’t have to think about it again for a while.
How long does an EPC last?
An EPC is valid for ten years., but if you’ve made significant changes to the property that affect energy use, like installing new windows or updating the heating system, you can always get a new EPC to reflect those changes.
How can you improve your EPC rating?
Improving your Energy Performance Certificate (EPC) rating is a great way to make your property more energy-efficient, reduce utility bills and increase its overall value. Here are some practical steps:
1. Add or upgrade your insulation
If your floors, walls or loft don’t have insulation, or don’t have the right type of insulation, then installing or upgrading this can significantly reduce heat loss.
2. Install double or even triple glazing
Windows with double or triple glazing keep more heat in and reduce draughts, which cuts energy loss.
3. Upgrade your heating system
Replacing an old, inefficient boiler with a condensing boiler can have an enormous boost to your EPC rating. In addition, installing heating controls or a smart thermostat can further improve heating efficiency.
4. Switch to LED lighting
LED bulbs use far less energy and last longer than traditional lighting, which is a quick and cost-effective upgrade.
5. Add renewable energy sources
Adding solar panels or an air source heat pump to your home can significantly reduce your reliance on non-renewable energy and improve your energy efficiency.
Is an EPC a legal requirement?
There are exemptions for certain dwellings (something we’ll cover below), but in most cases, yes, an EPC is a legal requirement. Anyone selling or renting a property must have an EPC when the property is listed for sale or rent.
If you’re legally required to have an EPC and don’t have one, you could face a fine. This penalty can range from £500 to £5,000.
When is an EPC not required?
Not every property needs an EPC. Exemptions include:
- Listed buildings.
- Buildings used as places of worship.
- Detached buildings with under 50 square metres of floor space.
- Holiday accommodation that is rented out less than 4 months of the year.
- Temporary buildings that will be used for 2 years or less.
EPC rating for new build homes
If you want an energy efficient home, then look no further than a new build. New build houses are designed and built to be more energy efficient, from the materials used to the technology installed inside them. Thermal insulation, solar panels, air source heat pumps, new heating systems, LED lighting; all are commonplace in a new build house.
On average, a new build house emits 67% less carbon compared to an older house. That's a saving of £82 per month and £979 per year! So if you want to reduce your environmental impact and save money, a new build makes a great deal of sense.
Our homes have an average EPC rating of B, meaning you’re getting an efficient home that is built to service your current and future needs.
